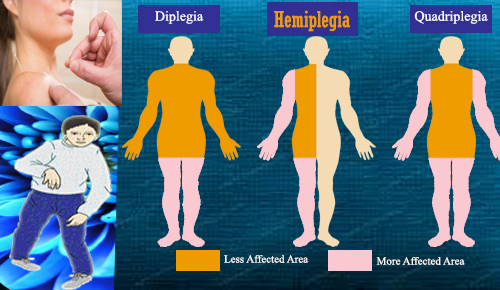
What is Hemiplegia?
Hemiplegia is a total paralysis of the arms, legs on the same side of the body. Hemiplegia worse than hemiparesis, where half of the body has less weaknesses. Hemiplegia may be congenital or acquired from a disease or stroke. Hemiplegia is not the usual health problems. In individuals older, stroke is the most common cause of hemiplegia. In children, the majority of cases of hemiplegia have not an identifiable causes and occur with a frequency of about one in every thousand births.
Causes of Hemiplegia
The most common cause is stroke. Stroke can cause a variety of movement disorders, depending on the location. Hemiplegia is common when a stroke affects kortikospinal channels. Other causes of hemiplegia including spinal cord injury. Hemiplegia occurs in the brain or spinal cord, as well as other disease that show the same impression. Another feature of weaknesses including decreased motion control, clonus (a series of involuntary muscle contractions that are very fast), spasticity, deep tendon reflexes exaggerated and decreased endurance.
Other cause of hemiplegia in adults include traume, cerebral hemorrhage, infection and cancer. Individuals who have uncontrolled diabetes, hypertension or those who are smoker have a chance of stroke. Weakness on one side of the face may occur and may be due to virus infection, stroke or cancer.
Signs and Symptoms Hemiplegia
- Difficult an ability balancewhile standing or walking
- Difficulty holding, grasping or pinching
- Decreased muscle strength
- Muscle spasms
- Difficulty to speaking
- Difficulty swallowing food
- Significant delays in reaching developmental milestones such as standing, smiling, crawling or speak
- Most children who suffer from hemiplegia also have abnormal mental development
- Behavioral problems such as anxiety, anger, irritability, lack of concentration or understanding
- Emotions – depression
- Shoulder pain – Often associated with loss of external rotation of the glenohumeral joint